Guidelines for the treatment of personal data in artificial intelligence

By: María del Pilar Duplat – Peña Mancero Abogados
In June 2019, the Superintendence of Industry and Commerce (hereinafter “SIC”) issued its Guidelines for the treatment of personal data through Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Purpose of the Guidelines
The guidelines seek to provide a series of suggestions to those who develop artificial intelligence projects based on the Standards for Data Protection for the Iberoamerican States of the Ibero-American Data Protection Network (RIPD, after its acronym in Spanish).
- Recommendations
- To comply with local regulation on the treatment of personal data
To avoid any legal objection over the AI products, it is important that your organization develop from the beginning a legal risk study of the local regulations to determine a strategy to:
- Mitigate legal risks.
- Earn and maintain the trust of the users of the AI technologies.
- Prevent any damage to the reputation of the organization.
- Avoid potential investigations from data protection or other authorities.
- To develop privacy impact studies
Before designing and developing AI products and to the extent possible, if there is a high risk of affecting the data protection rights of the owners of the data, it is necessary to develop a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA) to put in place an effective system of risk management and internal controls to guarantee that the data is dully treated and in compliance with the current regulation.
Said PIA must contain at least the following:
- A detailed description of the operations of treatment of personal data involved in the development of the AI.
- An evaluation of the specific risks for the rights and liberties of the owners of the personal data.
- The measures foreseen to face the risks, including the guarantees, safety measures, software design, technologies and mechanisms that guarantee the protection of the personal data, taking into consideration the legitimate interests and rights of the owners of the data and other potentially affected third parties.
The results of the PIA with the risk mitigation measures are part of the principle of privacy by design and by default.
- To include the privacy, ethics and security from the design and by default
The privacy by design and by default is considered as a proactive measure towards the Principle of Accountability. By including the privacy from the design, the organization seeks to guarantee the adequate treatment of the personal data used in the AI procedures, even before the risks are materialized.
Thus, the privacy by design must be included in the design, the architecture of the software or the algorithm of the AI product. The following are the purposes that the technology must include:
- Avoid unauthorized access to the data.
- Avoid the manipulation of the data.
- Avoid the destruction of the information.
- Avoid unauthorized or improper uses of the information.
- Avoid the circulation or supply of the data to unauthorized people.
The safety measures must be adequate and must consider various risk factors, such as:
- The risk levels of the treatment of data for the exercise of the rights and freedoms of the owners of the data.
- The nature of the data.
- The potential consequences derived from a safety breach and the magnitude of the damage caused by said breach to the owner and, overall, to the society.
- The number of owners of the data and the amount of information.
- The size of the organization.
- The available resources.
- The monitoring and follow-up of the reliability of the algorithms.
- The status of the technique
- The reach, context and purposes of the treatment of the information.
- The cross-border circulation of the data.
- The uncertainty and complexity of each AI initiative.
- Every safety measure must be revised, evaluated and permanently improved.
The following are risk management aspects that have an impact on the algorithms:
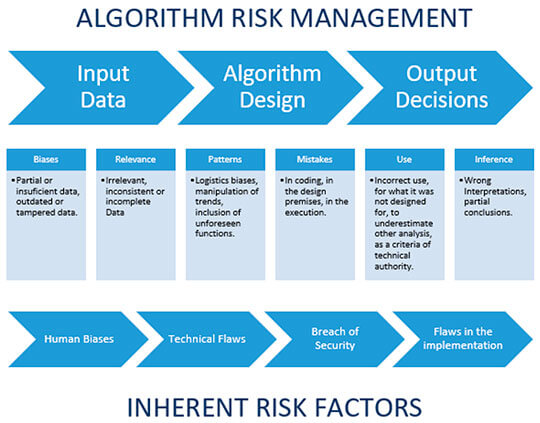
- To materialize the principle of accountability
The designers and developers of AI products must adopt useful, appropriate and affective measures to comply with their legal obligations. They must also show the evidence of the correct compliance of their duties. Said tools must be subject to permanent revision and evaluation to determine their effectiveness regarding the compliance and degree of protection of the personal data.
For said purpose, and to comply with the principle of accountability, the organization should have, at least the following:
- Allocate resources to implement data protection programs and policies.
- Implement a risk management program for the treatment of data protection.
- Develop mandatory data protection programs and policies within the organization.
- Put in place training and updating programs for the personnel on the obligations of data protection.
- Review periodically the policies and programs for the safety of the data to determine the required amendments.
- Incorporate an internal and external surveillance system, including audits, to verify the compliance of the data protection programs and policies.
- Establish procedures to receive and answer questions and complaints of the owners of the data.
The accountability principle goes further than just creating a series or policies and programs, it requires that the organization responsible for the treatment of the data can show evidence of concrete results of the correct treatment of the personal data in the AI projects.
- To design adequate governance schemes over the treatment of personal data in the entities who develop AI products.
It is recommended that the organization defines a structure with clear functions and responsibilities that guarantee a proper corporate governance for the respectful treatment of the norms related to the personal data protection regime and the rights of the owners of the data.
The main functions and responsibilities that must be set within the organization are the following:
-
- Develop risk management evaluations.
- Decide which decision-taking models will be used.
- Develop maintenance, monitoring and revision activities.
- Review the channels of communication with the users and consumers.
- To undertake measures to guarantee the principles of data protection in the AI Projects
Every person or organization responsible or in charge of the treatment of personal data must foresee adequate and efficient strategies to guarantee the compliance of the principles of treatment of personal data pursuant to the principles of the Standards for Data Protection for the Ibero-American States of the RIPD.
- To respect the rights of the owners and implement effective mechanisms so they can exercise them.
The organizations that create or use AI technologies must guarantee the following rights to the owners of the personal data:
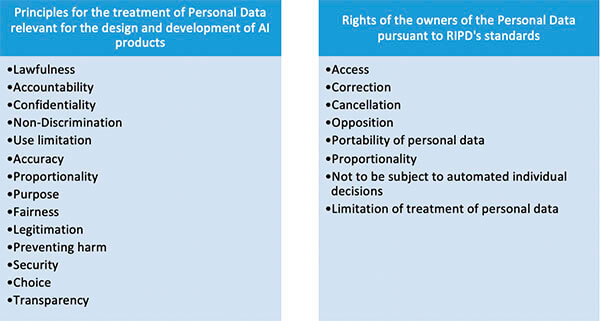
It is specially important to talk about the right “not to be subject to automated individual decisions” when we talk about AI proyects. Thus, when talking about AI projects, it must be a possibility for the owners of the personal data to argue any decision related to the treatment of his/her personal data before a human being, and that it is not 100% in charge of algorithms or automated procedures.
Additionally, the RIPD’s Standards forbid that the automated decisions are discriminatory. Thus, developers of the AI proyects must foresee in their design all the mechanisms or options for the owners of the data to exercise their rights through simple, free, fast, and accesible means that allow them to access, rectify, cancell, opose or transfer their personal data.
- To ensure the quality of the data
One of the risks using AI is that the machine is biased due to the configuration of the algorithm and the quality of the information. To minimize the risk of bias and prevent the breach of the rights of the owners of the personal data, it is suggested that:
- The information used by the AI is true and precise.
- The organization carries a registration of the source of the data.
- The organization makes audits of the sets of data used in the creation of the algorithms used in the decision-making processes by the machine.
- Grant veracity scores to the sets of data used to train the machine during its creation.
- Regularly update the data.
- Have separate sets of data to train, prove, and validate the decision-making processes.
- To use anonymization tools
It is important to determine if it is strictly necessary that the information that will be used by the AI must be used or linked to a person. If it is not necessary it is recommended that the information is used anonymously, so the owner of the data is not identified. In this way, the anonymization will help in the mitigation of the risks of massive treatment of personal data in the AI projects and procedures.
- To increase the trust and transparency with the owners of the personal data
A transparent organization may increase the trust of the owners of the Data in it through:
-
- Keeping open communication channels with Data owners and disclosing its policy for the treatment of the personal data in AI procedures or products. It is important to use a simple language that a non-expert in AI may understand.
- Carrying out pilot tests to evaluate the decision-making model and correct any problem that may exist.
- Giving the option to the data owner, in certain cases, that its information is excluded from the data provided and studied by the machine in the development of the algorithms and patterns in the cases allowed by law.
- Implementing revision channels so the decisions taken by the machine may be revised by humans to ratify them or correct them.
CAUSE FOR DISOLUTION OF COMPANIES DUE TO NON-COMPLIANCE WITH THE HYPOTHESIS OF CONTINUING BUSINESS


